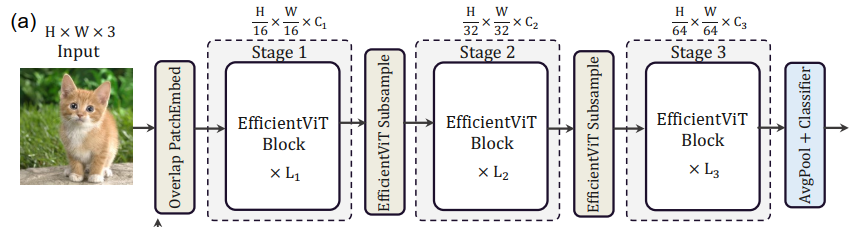
3.1. EfficientViT Building Blocks 这里主要介绍提出的EfficientViT block,也就是overlapping patch embedding之后的部分。
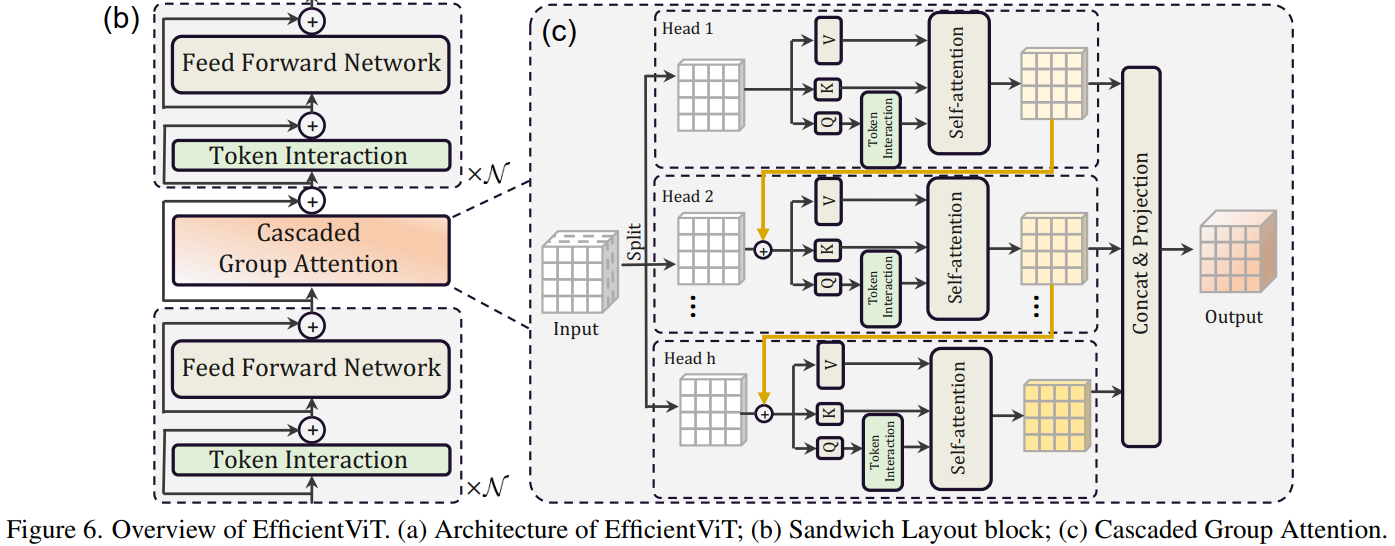
EfficientViT block 主要由一个称为 Sandwich Layout 结构构成。用了更少的memory-bound内存受限的self-attention layers 和更多的memory-efficient 的FFN layers来用于通道交流。也就是两个FFN中间夹一个Cascaded Group Attention。每个FFN之前用一个depthwise convolution (DWConv) 作为Token Interaction。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class EfficientViTBlock (torch.nn.Module): """ A basic EfficientViT building block. Args: type (str): Type for token mixer. Default: 's' for self-attention. ed (int): Number of input channels. kd (int): Dimension for query and key in the token mixer. nh (int): Number of attention heads. ar (int): Multiplier for the query dim for value dimension. resolution (int): Input resolution. window_resolution (int): Local window resolution. kernels (List[int]): The kernel size of the dw conv on query. """ def __init__ (self, type , ed, kd, nh=8 , ar=4 , resolution=14 , window_resolution=7 , kernels=[5 , 5 , 5 , 5 ], ): super ().__init__() self.dw0 = Residual(Conv2d_BN(ed, ed, 3 , 1 , 1 , groups=ed, bn_weight_init=0. , resolution=resolution)) self.ffn0 = Residual(FFN(ed, int (ed * 2 ), resolution)) if type == 's' : self.mixer = Residual(LocalWindowAttention(ed, kd, nh, attn_ratio=ar, \ resolution=resolution, window_resolution=window_resolution, kernels=kernels)) self.dw1 = Residual(Conv2d_BN(ed, ed, 3 , 1 , 1 , groups=ed, bn_weight_init=0. , resolution=resolution)) self.ffn1 = Residual(FFN(ed, int (ed * 2 ), resolution)) def forward (self, x ): return self.ffn1(self.dw1(self.mixer(self.ffn0(self.dw0(x)))))
Cascaded Group Attention :将输入从通道维度上分块,送入不同的head,分别进行self-atention,但同时上一个输出会和下一个的输入相加,然后将每个输出concat一起,最后通过一个linear layer将输出特征的维度与输入统一。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 B, C, H, W = x.shape trainingab = self.attention_biases[:, self.attention_bias_idxs] feats_in = x.chunk(len(self.qkvs), dim=1) # 分块 feats_out = [] feat = feats_in[0] for i, qkv in enumerate(self.qkvs): if i > 0: # add the previous output to the input feat = feat + feats_in[i] feat = qkv(feat) q, k, v = feat.view(B, -1, H, W).split([self.key_dim, self.key_dim, self.d], dim=1) # B, C/h, H, W q = self.dws[i](q) q, k, v = q.flatten(2), k.flatten(2), v.flatten(2) # B, C/h, N attn = ( (q.transpose(-2, -1) @ k) * self.scale + (trainingab[i] if self.training else self.ab[i]) ) attn = attn.softmax(dim=-1) # BNN feat = (v @ attn.transpose(-2, -1)).view(B, self.d, H, W) # BCHW feats_out.append(feat) x = self.proj(torch.cat(feats_out, 1))
3.2. EfficientViT Network Architectures 首先对输入的图像做overlapping patch embedding。
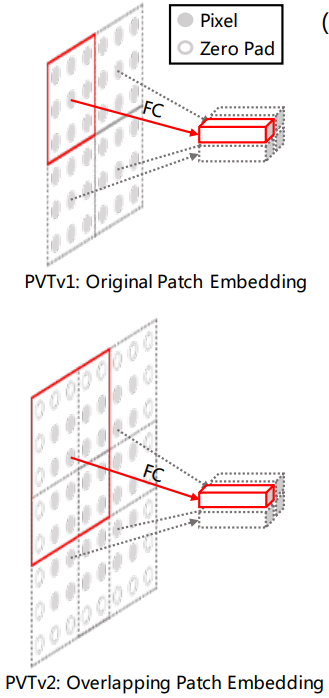
overlapping patch embedding来源于PVT v2: Improved Baselines with Pyramid Vision Transformer
先回顾一下原始ViT的patch embedding是怎么做的。假设输入图像的维度为(B, N, D) 的patch embedding, N是划分的patches的个数,D是embedding维度。
上述的操作等价于对输入图像
Overlapping Patch Embedding 是扩大Patch window,使得调整后的窗口有半个区域的重叠,而且把特征图用zero-padding来保持分辨率大小。也就是每个patch之间在原图是有重叠的。具体来说就是给定了一个输入大小为
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 self.patch_embed = torch.nn.Sequential( Conv2d_BN(in_chans, embed_dim[0 ] // 8 , 3 , 2 , 1 , resolution=resolution), torch.nn.ReLU(), Conv2d_BN(embed_dim[0 ] // 8 , embed_dim[0 ] // 4 , 3 , 2 , 1 , resolution=resolution // 2 ), torch.nn.ReLU(), Conv2d_BN(embed_dim[0 ] // 4 , embed_dim[0 ] // 2 , 3 , 2 , 1 , resolution=resolution // 4 ), torch.nn.ReLU(), Conv2d_BN(embed_dim[0 ] // 2 , embed_dim[0 ], 3 , 2 , 1 , resolution=resolution // 8 ))
其中Conv2d_BN(in_chans, out_chans, kernel_size, stride, pad, dilation, groups)。 若输入为(B, 3, 256, 256)的特征图,embed_dim[0]为64, 经过patch_embed得到(B, 64, 16, 16)。embed_dim的变化是3->8->16->32->64。
1 2 # x=[2,3,256,256] x1 = self.patch_embed(x) # x1=[2,64,16,16]